Level5day6-System V IPC 共享内存,消息队列与信号灯
1 System V IPC
IPC(Inter-Process Communication,进程间通讯)可以有三种信息共享方式(随文件系统,随内核,随共享内存)。(当然这里虽然说是进程间通讯,其实也是可以和线程相通的)。
相对的IPC的持续性(Persistence of IPC Object)也有三种:
-
1 随进程持续的(Process-Persistent IPC)
IPC对象一直存在,直到最后拥有他的进程被关闭为止,典型的IPC有pipes(管道)和FIFOs(先进先出对象)
-
2随内核持续的(Kernel-persistent IPC)
IPC对象一直存在直到内核被重启或者对象被显式关闭为止,在Unix中这种对象有System v 消息队列,信号量,共享内存。(注意Posix消息队列,信号量和共享内存被要求为至少是内核持续的,但是也有可能是文件持续的,这样看系统的具体实现)。
-
3.随文件系统持续的(FileSystem-persistent IPC)
除非IPC对象被显式删除,否则IPC对象会一直保持(即使内核才重启了也是会留着的)。如果Posix消息队列,信号量,和共享内存都是用内存映射文件的方法,那么这些IPC都有着这样的属性。
本节要学的System V IPC 属于第二类 随内核持续的信息共享方式。
IPC 对象包含: 共享内存、 消息队列 和 信号灯集
每个IPC对象有唯一的ID
IPC对象创建后一直存在,直到被显式地删除
每个IPC对象有一个关联的KEY
1.1 System V IPC 的控制台查询命令
ipcs and ipcrm Programs
由于System V IPC的三种类型不是以文件系统中的路径名标识的,所以标准的ls和rm程序无法看到他们,也没办法删除,不过任何实现了System V IPC的系统都提供了两个特殊的程序,ipcs和ipcrm,ipcs输出有关System V IPC特性的各种信息,ipcrm删除一个System V 消息队列,信号量或者共享内存区。
linux@ubuntu:~$ ipcs --------- 消息队列 ----------- 键 msqid 拥有者 权限 已用字节数 消息 ------------ 共享内存段 -------------- 键 shmid 拥有者 权限 字节 连接数 状态 0x4b05243a 7 linux 666 1024 1 0x00000000 10 linux 600 524288 2 目标 0x00000000 11 linux 600 524288 2 目标 0x00000000 17 linux 600 524288 2 目标 --------- 信号量数组 ----------- 键 semid 拥有者 权限 nsems 0x4b05243a 1 linux 666 2 linux@ubuntu:~$ ipcrm -s 0 linux@ubuntu:~$ ipcrm --help -m, --shmem-id <id> 按 id 号移除共享内存段 -M, --shmem-key <键> 按键值移除共享内存段 -q, --queue-id <id> 按 id 号移除消息队列 -Q, --queue-key <键> 按键值移除消息队列 -s, --semaphore-id <id> 按 id 号移除信号量 -S, --semaphore-key <键> 按键值移除信号量 -a, --all[=<shm|msg|sem>] (将指定类别中的)全部移除 -v, --verbose 解释正在进行的操作
1.2 key_t Keys和ftok Function
System V IPC系统创建新的IPC的三个函数分别是msgget(),senget(),shmget()这三个函数的参数都是(key_t key, int mode),其实key是由ftok函数创建的一个键值,ftok函数的声明为:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> key_t ftok(const char *pathname,int id); 成功时返回合法的key值,失败时返回EOF path 存在且可访问的文件的路径 proj_id 用于生成key的数字,范围1-255。
这个函数假定了这个程序使用了System V IPC进行通讯,客户端和服务器端同意使用具有一定意义的pathname(是已存在的路径名),如果客户端和服务器只用单一通道,那么可以将id为1;如果客户端和服务器需要双向通道(而且是两条),那么可以令一个通道的id为1,另一个为2,只要pathname是一样的,那可以认为客户端和服务器使用是同一种通道进行通讯的。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { key_t key; if ((key = ftok(“.”, ‘a’)) == -1) { perror(“key”); exit(-1); }
2 共享内存
共享内存是一种最为高效的进程间通信方式,进程可以直接读写内存,而不需要任何数据的拷贝 共享内存在内核空间创建,可被进程映射到用户空间访问,使用灵活 由于多个进程可同时访问共享内存,因此需要同步和互斥机制配合使用
2.1 共享内存使用步骤
创建/打开共享内存 映射共享内存,即把指定的共享内存映射到进程的地址空间用于访问 读写共享内存 撤销共享内存映射 删除共享内存对象
2.2 共享内存创建 – shmget
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int shmget(key_t key, int size, int shmflg); 成功时返回共享内存的id,失败时返回EOF key 和共享内存关联的key,IPC_PRIVATE 或 ftok生成 shmflg 共享内存标志位 IPC_CREAT|0666 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 示例1: 要求:创建一个私有的共享内存,大小为512字节,权限为0666 int shmid; if ((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 512, 0666)) < 0) { perror(“shmget”); //IPC_PRIVATE 参数表示是私有内存 exit(-1); } if ((pid = fork()) == -1) { perror("fork"); exit(-1); } 使用IPC_PRIVATE创建的IPC对象, key值属性为0,和IPC对象的编号就没有了对应关系。这样毫无关系的进程,就不能通过key值来得到IPC对象的编号(因为这种方式创建的IPC对象的key值都是0)。因此,这种方式产生的IPC对象,和无名管道类似,不能用于毫无关系的进程间通信。但也不是一点用处都没有,仍然可以用于有亲缘关系的进程间通信。使用IPC_PRIVATE方式注意 int shmID=shmget(IPC_PRIVATE,len,IPC_CREAT|0600); 需要在父子进程都可见的地方调用(即在创建子进程之前),否则不能实现内存的共享 因为通过IPC_PRIVATE这个key获得的id不一样,其他通过ftok获得的key来shmget获得的id在程序每次运行中是一样的。ftok参数一样的话每次程序运行中返回值都一样。 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 示例2: 要求:创建/打开一个和key关联的共享内存,大小为1024 字节,权限为0666 key_t key; int shmid; if ((key = ftok(“.”, ‘m’)) == -1) { perror(“ftok”); exit(-1); } if ((shmid = shmget(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT|0666)) < 0) { perror(“shmget”); exit(-1); }
2.3 共享内存映射 – shmat
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg); 成功时返回映射后的地址,失败时返回(void *)-1 shmid 要映射的共享内存id shmaddr 映射后的地址, NULL表示由系统自动映射 shmflg 标志位 0表示可读写;SHM_RDONLY表示只读
示例:在共享内存中存放键盘输入的字符串
char *addr; int shmid; …… if ((addr = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0)) == (char *)-1) { perror(“shmat”); exit(-1); } fgets(addr, N, stdin);
2.4 共享内存撤销映射 – shmdt
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int shmdt(void *shmaddr); 成功时返回0,失败时返回EOF 不使用共享内存时应撤销映射 进程结束时自动撤销
2.5 共享内存控制 – shmctl
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf); 成功时返回0,失败时返回EOF shmid 要操作的共享内存的id cmd 要执行的操作 IPC_STAT IPC_SET IPC_RMID buf 保存或设置共享内存属性的地址
2.6 共享内存其他注意事项
每块共享内存大小有限制 ipcs -l cat /proc/sys/kernel/shmmax linux@ubuntu:~/projects/Level5day6_2$ ipcs -l ---------- 消息限制 ----------- 系统最大队列数量 = 32000 最大消息尺寸 (字节) = 8192 默认的队列最大尺寸 (字节) = 16384 ---------- 同享内存限制 ------------ 最大段数 = 4096 最大段大小 (千字节) = 18014398509465599 最大总共享内存 (千字节) = 18014398509481980 最小段大小 (字节) = 1 --------- 信号量限制 ----------- 最大数组数量 = 32000 每个数组的最大信号量数目 = 32000 系统最大信号量数 = 1024000000 每次信号量调用最大操作数 = 500 信号量最大值=32767 linux@ubuntu:~/projects/Level5day6_2$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/shmmax 18446744073692774399 共享内存删除的时间点 shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL) 添加删除标记 nattach 变成0时真正删除
2.7 共享内存读写进程范例
#include <cstdio> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> /* *内存读写测试-读进程; */ char* path = "./"; int main() { key_t key = ftok(path, 75); int result; if (key == EOF) { perror("ftok"); return -1; } int id = shmget(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT|0666); if (id == EOF) { perror("shmget"); return -1; } void* pmem = shmat(id,NULL,0); if (pmem == (void*)-1) { perror("shmat"); return -1; } printf("Memory Message is:%s\n",(char*)pmem); sleep(10); result = shmdt(pmem); if (result == EOF) { perror("pmem"); return -1; } result = shmctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL); return 0; }
#include <cstdio> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> /* *内存读写测试-写进程; */ char* path = "./"; int main() { char botton[] = "Memory Share Success!"; key_t key = ftok(path, 75); int result; if (key == EOF) { perror("ftok"); return -1; } int id = shmget(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT|0666); if (id == EOF) { perror("shmget"); return -1; } void* pmem = shmat(id,NULL,0); if (pmem == (void*)-1) { perror("shmat"); return -1; } memcpy(pmem,botton,sizeof(botton)); sleep(10); result = shmdt(pmem); if (result == EOF) { perror("pmem"); return -1; } result = shmctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL); return 0; }
3 消息队列
消息队列是System V IPC对象的一种
消息队列由消息队列ID来唯一标识
消息队列就是一个消息的列表。用户可以在消息队列中添加消息、读取消息等
消息队列可以按照类型来发送/接收消息
3.1 消息队列使用步骤:
打开/创建消息队列 msgget
向消息队列发送消息 msgsnd
从消息队列接收消息 msgrcv
控制消息队列 msgctl
3.2 消息队列创建/打开 – msgget
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg); 成功时返回消息队列的id,失败时返回EOF key 和消息队列关联的key IPC_PRIVATE 或 ftok msgflg 标志位 IPC_CREAT|0666
示例:
int main() { int msgid; key_t key; if ((key = ftok(“.”, ‘q’)) == -1) { perror(“ftok”); exit(-1); } if ((msgid = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT|0666)) < 0) { perror(“msgget”); exit(-1); } …… return 0; }
3.3 消息发送 – msgsnd
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> int msgsnd(int msgid, const void *msgp, size_t size, int msgflg); 成功时返回0,失败时返回-1 msgid 消息队列id msgp 消息缓冲区地址 size 消息正文长度 msgflg 标志位 0 或 IPC_NOWAIT

示例:
typedef struct { long mtype; char mtext[64]; } MSG; #define LEN (sizeof(MSG) – sizeof(long)) int main() { MSG buf; …… buf.mtype = 100; fgets(buf.mtext, 64, stdin); msgsnd(msgid, &buf,LEN, 0); …… return 0; }
3.4 消息格式
-
通信双方首先定义好统一的消息格式
-
用户根据应用需求定义结构体类型
-
首成员类型必须为long,代表消息类型(正整数)
-
其他成员都属于消息正文
-
消息长度不包括首类型 long
3.5 消息接收 – msgrcv
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> int msgrcv(int msgid, void *msgp, size_t size, long msgtype, int msgflg); 成功时返回收到的消息长度,失败时返回-1 msgid 消息队列id msgp 消息缓冲区地址 size 指定接收的消息长度 msgtype 指定接收的消息类型 msgflg 标志位 0 或 IPC_NOWAIT

范例:
typedef struct { long mtype; char mtext[64]; } MSG; #define LEN (sizeof(MSG) – sizeof(long)) int main() { MSG buf; …… if (msgrcv(msgid, &buf,LEN, 200, 0) < 0) { perror(“msgrcv”); exit(-1); } …… }
3.6 控制消息队列 – msgctl
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> int msgctl(int msgid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf); 成功时返回0,失败时返回-1 msgid 消息队列id cmd 要执行的操作 IPC_STAT / IPC_SET / IPC_RMID buf 存放消息队列属性的地址
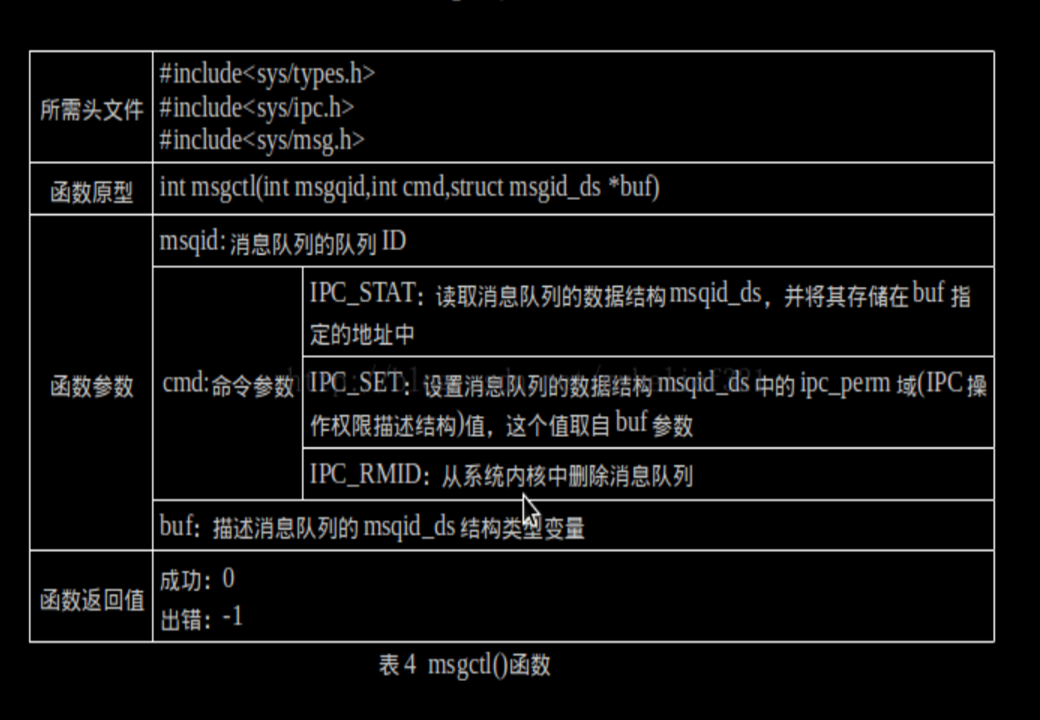
3.7 范例
消息队列发送端
#include <cstdio> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> char* path = "./"; char* botton = "Message List test success!\n"; typedef struct { long mtype; char mtext[64]; } MSG; #define LEN (sizeof(MSG) - sizeof(long)) int main() { int result,id; MSG buf; key_t key = ftok(path, 75); if (key == EOF) { perror("ftok"); return -1; } id = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | 0666); if (id == EOF) { perror("msgget"); return -1; } buf.mtype = 100; strcpy(buf.mtext, botton); result = msgsnd(id, &buf, LEN, 0); if (result == EOF) { perror("msgsnd"); return -1; } sleep(10); msgctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL); return 0; }
消息队列接收端
#include <cstdio> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> char* path = "./"; char* botton = "Message List test success!\n"; typedef struct { long mtype; char mtext[64]; } MSG; #define LEN (sizeof(MSG) - sizeof(long)) int main() { int result,id; MSG buf; key_t key = ftok(path, 75); if (key == EOF) { perror("ftok"); return -1; } id = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | 0666); if (id == EOF) { perror("msgget"); return -1; } buf.mtype = 100; result = msgrcv(id,&buf,LEN,0,0); if (result == EOF) { perror("msgrcv"); return -1; } printf("%s\n",buf.mtext); sleep(10); msgctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL); return 0; }
4. System V IPC - 信号灯
信号灯也叫信号量,用于进程/线程同步或互斥的机制
信号灯的类型
Posix 无名信号灯(前面线程学过)
Posix有名信号灯
System V 信号灯
信号灯的含义
计数信号灯(1和2都是)
System V信号灯是一个或多个计数信号灯的集合(可操作集合中的多个信号灯)
4.1 信号灯创建/打开 – semget
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg); 成功时返回信号灯的id,失败时返回-1 key 和消息队列关联的key IPC_PRIVATE 或 ftok nsems 集合中包含的计数信号灯个数 semflg 标志位 IPC_CREAT|0666 IPC_EXCL
union semun { int val; /* Value for SETVAL */ struct semid_ds *buf; /* Buffer for IPC_STAT, IPC_SET */ unsigned short *array; /* Array for GETALL, SETALL */ struct seminfo *__buf; /* Buffer for IPC_INFO (Linux-specific) */ };
4.2 信号灯初始化 – semctl
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> int semctl(int semid, int semnum, int cmd, …); 成功时返回0,失败时返回EOF semid 要操作的信号灯集id semnum 要操作的集合中的信号灯编号 cmd 执行的操作 SETVAL IPC_RMID union semun 取决于cmd
示例
要求:假设信号灯集合中包含两个信号灯;
第一个初始化为2,第二个初始化为0
union semun myun; myun.val = 2; if (semctl(semid, 0, SETVAL, myun) < 0) { perror(“semctl”); exit(-1); } myun.val = 0; if (semctl(semid, 1, SETVAL, myun) < 0) { perror(“semctl”); exit(-1); }
4.3 信号灯P/V操作 – semop
#include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> int semop(int semid, struct sembuf *sops, unsigned nsops); 成功时返回0,失败时返回-1 semid 要操作的信号灯集id sops 描述对信号灯操作的结构体(数组) nsops 要操作的信号灯的个数
4.3.1 信号灯操作 – sembuf
struct sembuf { short sem_num; short sem_op; short sem_flg; }; semnum 信号灯编号 sem_op -1:P操作 1:V操作 sem_flg 0 / IPC_NOWAIT
4.4 信号灯集/共享内存 - 示例
要求:父子进程通过System V信号灯同步对共享内存的读写
父进程从键盘输入字符串到共享内存
子进程打印字符串
父进程输入quit后删除共享内存和信号灯集,程序结束
注意:本程序 如果没有正常退出,第二次执行的时候 需要使用 ipcrm -s 清理掉信号灯集才能获取正常结果。
#include <cstdio> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include <sys/sem.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #define NUM 1024 #define SEM_READ 0 #define SEM_WRITE 1 char* PATH = "./"; char Botton[NUM] = "test success!"; union semun { int val; /* Value for SETVAL */ struct semid_ds* buf; /* Buffer for IPC_STAT, IPC_SET */ unsigned short* array; /* Array for GETALL, SETALL */ struct seminfo* __buf; /* Buffer for IPC_INFO (Linux-specific) */ }; union semun myun; int main() { key_t key = ftok(PATH,75); int shmid,result,semid,i; char* pshm = NULL; pid_t pid; if (key == EOF) { perror("ftok"); return -1; } semid = semget(key, 2, IPC_CREAT | 0666); if (semid == EOF) { perror("semget"); return -1; } myun.val = 0; result = semctl(semid,SEM_READ, SETVAL, myun); if (result == EOF) { perror("semctl"); return -1; } myun.val = 1; result = semctl(semid, SEM_WRITE, SETVAL, myun); if (result == EOF) { perror("semctl"); return -1; } shmid = shmget(key, NUM, IPC_CREAT | 0666); if (shmid == EOF) { perror("shmget"); return -1; } pshm = (char*)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); if (pshm == (char*)-1) { perror("pshm"); return -1; } pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { perror("fork"); return -1; } else if (pid > 0) { struct sembuf mybuf_Read; struct sembuf mybuf_Write; i = 0; mybuf_Read.sem_flg = 0; mybuf_Read.sem_num = SEM_READ; mybuf_Read.sem_op = 1; mybuf_Write.sem_flg = 0; mybuf_Write.sem_num = SEM_WRITE; mybuf_Write.sem_op = -1; while (1) { result = semop(semid, &mybuf_Write, 1); if (result == EOF) { perror("semop"); return -1; } printf("please input char to shm:"); fgets(pshm, 64, stdin); //strcpy(pshm, Botton); result = semop(semid, &mybuf_Read, 1); if (result == EOF) { perror("semop"); return -1; } } } else { struct sembuf mybuf_Read; struct sembuf mybuf_Write; i = 0; mybuf_Read.sem_flg = 0; mybuf_Read.sem_num = SEM_READ; mybuf_Read.sem_op = -1; mybuf_Write.sem_flg = 0; mybuf_Write.sem_num = SEM_WRITE; mybuf_Write.sem_op = 1; while (1) { result = semop(semid, &mybuf_Read, 1); if (result == EOF) { perror("semop"); return -1; } printf("shm:%s\n", pshm); result = semop(semid, &mybuf_Write, 1); if (result == EOF) { perror("semop"); return -1; } } } result = shmdt(pshm); if (result == EOF) { perror("shmdt"); return -1; } result = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID,0); return 0; }
参考文档
UNIX 进程间通讯(IPC)概念(Posix,System V IPC): https://www.cnblogs.com/Philip-Tell-Truth/p/6284475.html
ftok()函数深度解析: https://blog.csdn.net/u013485792/article/details/50764224